Configuring Cisco devices
to use a ClockWatch NTP server
|
You can use
ClockWatch ServerMP as an NTP time server to
synchronize time on a variety of devices including networking equipment
such as Cisco routers and switches.
Network Time Protocol (NTP) allows routers on your network to
synchronize their time settings with an NTP server. |
 |
|
A group of NTP clients that obtains time and date information from a
single source will have more consistent time settings. |
Cisco IOS
The more recent versions of IOS (version 10+) support NTP
version 4.
To make your router synchronize with a ClockWatch NTP
server with the IP address of 192.168.1.1, use the IOS commands:
Router>
enable
password:
*********
Router# config t
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.1
Router(config)# exit
Router# wr
mem
The NTP server
command forms a server association with the ClockWatch server. The Cisco
router then goes through the process of validating the ClockWatch
server. This may be immediate or take several minutes. You can confirm
it has been synchronized by showing the NTP associations:
Router>show ntp associations
address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp
*~192.168.1.1 .CLKW. 1 35 64 377 23.9 -0.45 1.2
The star (*) displayed next to the configured
(~) peer indicates the router is synchronized
with ClockWatch. A pound sign (#) indicates that the router isn't
syncing with ClockWatch even though NTP request and response packets
are being exchanged. In this case, check the output of the show ntp
associations detail command or enable the NTP debugs to see why the
clocks aren't syncing.
One possible reason for the failure to sync is that the NTP client's clock
differs by more than 4000 seconds from ClockWatch's clock. On Cisco
routers, a time difference of greater than 4000 seconds is considered out
of range, and prevents the router from syncing to the server. This
doesn't apply when you first configure an NTP peer on a Cisco router or
at a reload. In this case, the NTP client's (the Cisco router's) clock
is changed to match the NTP server's clock, no matter how large the
difference.
Tips:
-
Check that ClockWatch
Server has been synchronized to
an external timeserver within the last 24 hours. This is a
NTP server qualification requirement of the Cisco NTP client
implementation.
-
ClockWatch does not support authentication.
Turn off authentication by issuing the IOS configuration command
no ntp authentication. Authentication is normally
turned on in IOS version 12.4 and above.
-
You can manually change the client's clock
(using the clock set command) to within a
few minutes of the ClockWatch Server's clock to facilitate the
synchronization.
-
Make sure you check the time zone of the
client's clock; local time is displayed, but time values in NTP
messages are stored in UTC (GMT).
For a more detailed listing of NTP status, use the
show ntp associations detail command:
Router>show ntp associations detail
192.168.1.1 configured, our_master, sane, valid, stratum 1
ref ID .CLKW., time C6124378.B35E47B9 (15:21:28.700 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
our mode client, peer mode server, our poll intvl 64, peer poll intvl 16
root delay 1003.92 msec, root disp 3.92, reach 377, sync dist 519.028
delay 23.88 msec, offset -0.4462 msec, dispersion 1.21
precision 2**18, version 3
org time C61255D6.AFDF0000 (16:39:50.686 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
rcv time C61255D6.B30ADC84 (16:39:50.699 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
xmt time C61255D6.ACEDE6D8 (16:39:50.675 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
filtdelay = 23.88 24.12 28.26 23.90 23.77 24.83 24.63 24.02
filtoffset = -0.45 -1.59 -0.55 1.01 0.45 1.74 -0.44 1.71
filterror = 0.02 0.99 1.97 2.94 3.92 3.94 3.95 3.97
NTP detail that describes the
connection as 'insane' (vs. sane) means that the client has yet to be
synchronized with the server.
Cisco Security Device Manager (SDM)
The NTP server can also
be set in Cisco's GUI interface, SDM.
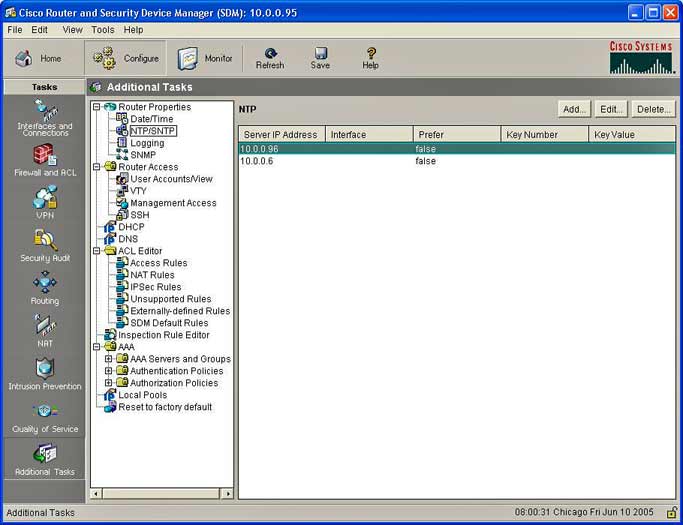
Cisco Security Device Manager - Additional Task Configuration Screen
To set the NTP server open SDM, press
'Configure', open 'Additional Tasks', choose 'Router Properties' and
then "NTP/SNTP." If your router does not support NTP commands, the
NTP/SNTP branch will not appear in the Router Properties tree. You may
be able to upgrade to a later version of IOS and add this capability.
NTP/SNTP Properties
This window allows you to view the NTP server information that has been
configured, to add new information, or to edit or delete
existing information.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the ClockWatch Server.
Interface
The interface over which the router will communicate with the
ClockWatch server.
Preferred
Preferred NTP servers will be contacted before non-preferred
servers. There can be more than one preferred NTP server. |
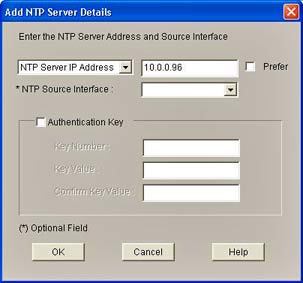 |
| You can then press "OK" to add
the NTP server. |
|
Configuring for SNTP
SNTP is Simple Network Time Protocol, a
simplified version of NTP. ClockWatch Server can also act as an
SNTP server for Cisco NTP clients.
To configure SNTP from IOS:
Router>
enable
password:
*********
Router# config terminal
Router(config)# sntp server 10.10.10.96
Router(config)# exit
Router# wr
mem
Troubleshooting NTP Clients
|
Run the show ntp associations detail
command to check the status of Client/Server communication (see
instructions above) and check the resulting output (see
sample above) for the following:
-
Check for correct IP
address of ClockWatch
Server, check status (sane or insane):
192.168.1.1 configured, our_master, sane, valid, stratum 1
Check for the proper server reference ID of
ClockWatch (CLKW), check that the last time the ClockWatch
server was synced (the time in parentheses) was within the last
24 hours:
ref ID .CLKW., time C6124378.B35E47B9 (15:21:28.700 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
Check that there are valid times shown for the
origination and receive time. These are times sent by
ClockWatch Server. Empty or nonsense times could mean a connection problem
our could mean that authentication is enabled (see below).
org time C61255D6.AFDF0000 (16:39:50.686 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
rcv time C61255D6.B30ADC84 (16:39:50.699 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
-
The transmit (xmt) time value comes from the
client. It should be within 1 day of the correct date and time
to facilitate syncing of the client:
xmt time C61255D6.ACEDE6D8 (16:39:50.675 UTC Thu Apr 21 2005)
|
| ClockWatch does not support NTP client authentication.
Turn off authentication by issuing the IOS configuration command
no ntp authentication. Authentication is normally
turned on in IOS version 12.4 and above. |
| Run the debug ntp validity command
to get detail on why ClockWatch Server is not being qualified as
a server. This trace will report information on what qualifying
tests the server is failing.
Validity
(sanity) tests are specified in the NTP RFC1305 to test the
reply packet received.
Eight of them are defined and when you do a debug ntp
validity each of those failed test
is being represent by a received bit.
Test Meaning
1 Duplicate packet received
2 Bogus packet received
3 Protocol unsynchronized
4 Peer delay/dispersion failed boundary check
5 Peer authentication failed
6 Peer clock unsynchronized (common for
un-synched server)
7 Peer stratum out of bounds
8 Root delay/dispersion failed boundary check
Test 1 to 3 check for
the validity of the data portion of the
packet.
Packet data is valid if test 1 to 4 are passed.
Then the data
will be used to calculate offset, delay, and the dispersion.
Tests 5 to 8 check the NTP header information.
If test 8 is failing it might mean the following problem with
root dispersion or delay.
* Root Dispersion: Maximum error relative to the primary reference source
at the root of the NTP subnet
* Root Delay: Total roundtrip delay to the primary reference source at the
root of the NTP subnet
Sample debug output:
NTP: packet from 192.168.1.101
failed validity tests 80
Root delay/dispersion failed boundary check |
CAT OS
To make your router synchronize with NTP servers with
IP addresses 192.168.1.1, use the commands:
ciscoswitch>
enable
password:
*********
ciscoswitch#
set ntp client enable
ciscoswitch# ntp server
192.168.1.1
ciscoswitch#
exit
The NTP server
command forms a server association with the
ClockWatch Server, and
set NTP client enable
activates the NTP client.
For more information on client/server communication:
ClockWatch ServerMP
ClockWatch
Client/Server


